Hyundai Santa Fe: Tires and wheels / Tire sidewall labeling
This information identifies and describes the fundamental characteristics of the tire and also provides the tire identification number (TIN) for safety standard certification. The TIN can be used to identify the tire in case of a recall.
.png)
1. Manufacturer or brand name
Manufacturer or brand name is shown.
2. Tire size designation
A tire’s sidewall is marked with a tire size designation. You will need this information when selecting replacement tires for your car. The following explains what the letters and numbers in the tire size designation mean.
Example tire size designation:
(These numbers are provided as an example only; your tire size designator could vary depending on your vehicle.)
235/60R18 102H
235 - Tire width in millimeters.
60 - Aspect ratio. The tire’s section height as a percentage of its width.
R - Tire construction code (Radial).
18 - Rim diameter in inches.
102 - Load Index, a numerical code associated with the maximum load the tire can
carry.
H - Speed Rating Symbol. See the speed rating chart in this section for additional
information.
Wheel size designation
Wheels are also marked with important information that you need if you ever have to replace one. The following explains what the letters and numbers in the wheel size designation mean.
Example wheel size designation:
7.5J X 18
7.5 - Rim width in inches.
J - Rim contour designation.
18 - Rim diameter in inches.
Tire speed ratings
The chart below lists many of the different speed ratings currently being used for passenger vehicle tires. The speed rating is part of the tire size designation on the sidewall of the tire. This symbol corresponds to that tire’s designed maximum safe operating speed.
.png)
3. Checking tire life (TIN : Tire Identification Number)
Any tires that are over six years old, based on the manufacturing date, (including the spare tire) should be replaced by new ones. You can find the manufacturing date on the tire sidewall (possibly on the inside of the wheel), displaying the DOT Code. The DOT Code is a series of numbers on a tire consisting of numbers and English letters. The manufacturing date is designated by the last four digits (characters) of the DOT code.
DOT : XXXX XXXX OOOO
The front part of the DOT shows a plant code number, tire size and tread pattern and the last four numbers indicate week and year manufactured.
For example:
DOT XXXX XXXX 1520 represents that the tire was produced in the 15th week of 2020.
4. Tire ply composition and material
The number of layers or plies of rubber-coated fabric in the tire. Tire manufacturers also must indicate the materials in the tire, which include steel, nylon, polyester, and others. The letter “R” means radial ply construction; the letter “D“ means diagonal or bias ply construction; and the letter “B” means belted-bias ply construction.
5. Maximum permissible inflation pressure
This number is the greatest amount of air pressure that should be put in the tire. Do not exceed the maximum permissible inflation pressure. Refer to the Tire and Loading Information label for recommended inflation pressure.
6. Maximum load rating
This number indicates the maximum load in kilograms and pounds that can be carried by the tire. When replacing the tires on the vehicle, always use a tire that has the same load rating as the factory installed tire.
7. Uniform tire quality grading
Quality grades can be found where applicable on the tire sidewall between tread shoulder and maximum section width.
For example:
TREADWEAR 200
TRACTION AA
TEMPERATURE A
Tread wear
The tread wear grade is a comparative rating based on the wear rate of the tire when tested under controlled conditions on a specified government test course. For example, a tire graded 150 would wear one-and-a-half times (1½) as well on the government course as a tire graded 100.
The relative performance of tires depends upon the actual conditions of their use, however, and may depart significantly from the norm due to variations in driving habits, service practices and differences in road characteristics and climate.
These grades are molded on the sidewalls of passenger vehicle tires. The tires available as standard or optional equipment on your vehicle may vary with respect to grade.
Traction - AA, A, B & C
The traction grades, from highest to lowest, are AA, A, B and C. Those grades represent the tire’s ability to stop on wet pavement as measured under controlled conditions on specified government test surfaces of asphalt and concrete. A tire marked C may have poor traction performance.
WARNING
The traction grade assigned to this tire is based on straight ahead braking traction tests, and does not include acceleration, cornering, hydroplaning, or peak traction characteristics.
Temperature - A, B & C
The temperature grades are A (the highest), B and C representing the tire’s resistance to the generation of heat and its ability to dissipate heat when tested under controlled conditions on a specified indoor laboratory test wheel.
Sustained high temperature can cause the material of the tire to degenerate and reduce tire life, and excessive temperature can lead to sudden tire failure. Grades B and A represent higher levels of performance on the laboratory test wheel than the minimum required by law.
WARNING
The temperature grade for this tire is established for a tire that is properly inflated and not overloaded. Excessive speed, under-inflation, over-inflation, or excessive loading, either separately or in combination, can cause heat buildup and possible sudden tire failure. This may cause loss of vehicle control resulting in an accident.
 Wheel replacement. Tire traction. Tire maintenance
Wheel replacement. Tire traction. Tire maintenance
Wheel replacement
When replacing the metal wheels for any reason, make sure the new wheels are
equivalent to the original factory units in diameter, rim width and offset...
 Low aspect ratio tires
Low aspect ratio tires
The aspect ratio is lower than 50 on low aspect ratio tires.
Because low aspect ratio tires are optimized for handling and braking, their
sidewall is a little stiffer than a standard tire...
Other information:
Hyundai Santa Fe (TM) 2019-2025 Owner's Manual: System operation
Operating conditions Smart Cruise Control will operate when the following conditions are satisfied. Basic function The gear is in D (Drive) The driver’s door is closed EPB (Electronic Parking Brake) is not applied Your vehicle speed is within the operating speed range -- 5~110 mph (10~180 km/h): when there is no vehicle in front -- 0~110 mph (0~180 km/h): when there is a vehicle in front ESC (Electronic Stability Control), TCS (Traction Control System) or ABS is on ESC (Electronic Stability Control), TCS (Traction Control System) or ABS is not controlling the vehicle Engine rpm is not in the red zone Forward Collision-Avoidance Assist brake control is not operating Remote Smart Parking Assist brake control is not operating Information At a stop, if there is no vehicle in front of your vehicle, the system will turn on when the brake pedal is depressed...
Hyundai Santa Fe (TM) 2019-2025 Service Manual: Mechanism Rail. Repair procedures
Replacement 1. Remove the roof trim. 2. Remove the movable glass. (Panorama sunroof - refer "Movable Glass") 3. Remove the roller blind...
Categories
- Manuals Home
- 4th Generation Santa Fe Owners Manual
- 4th Generation Santa Fe Service Manual
- Brake bleeding procedures
- Resetting the power liftgate
- Warning and indicator lights
- New on site
- Most important about car
Air bag - supplemental restraint system
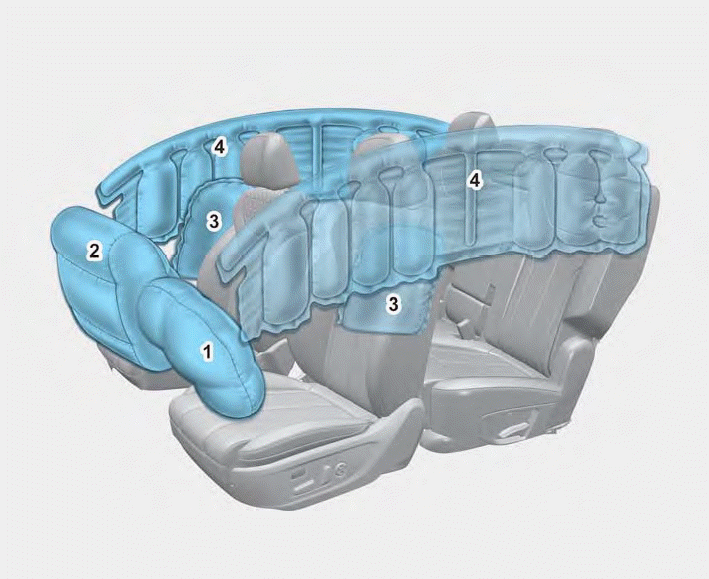
1. Driver’s front air bag
2. Passenger’s front air bag
3. Side air bag
4. Curtain air bag
The vehicles are equipped with a Supplemental Air Bag System for the driver’s seat and front passenger’s seats.
The front air bags are designed to supplement the three-point seat belts. For these air bags to provide protection, the seat belts must be worn at all times when driving.
